Oral Cancer and Head & Neck Cancer
Oral Cancer
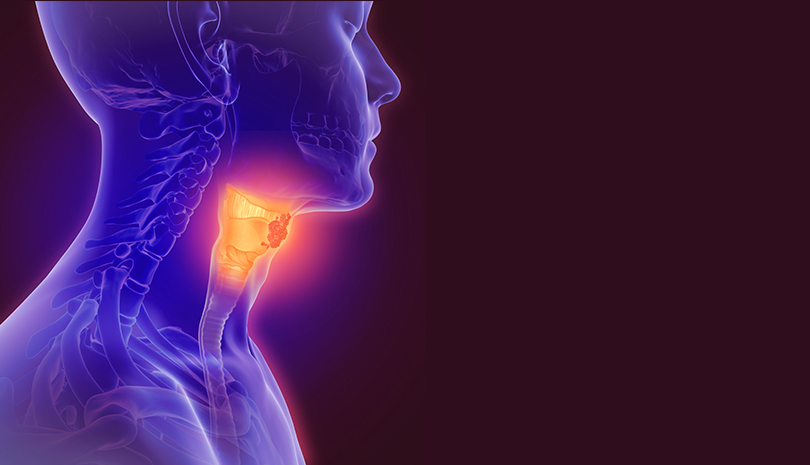
What is Oral Cancer?
Oral cancer, also known as mouth cancer, refers to cancer that develops in any part of the oral cavity — including the lips, gums, tongue, inner cheeks, floor or roof of the mouth, and the throat's upper part (oropharynx). It typically begins in the flat, thin squamous cells lining the mouth and can spread rapidly if not detected early.
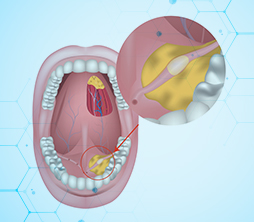
Who is at Risk?
Oral cancer most commonly affects people over 40, especially males, but it can occur in younger individuals too. The disease is often linked to lifestyle risk factors and can be more aggressive in people with poor general health.
There are two primary types of uterine cancer:
Oral cancer may be classified based on the type of cells involved or the site affected:
Signs and Symptoms
Oral cancer symptoms can be subtle at first but become more pronounced over time. Common signs include:
Risk Factors
The main risk factors associated with oral cancer include:
Preventing Oral Cancer
While oral cancer may not be entirely preventable, several strategies can lower your risk:
Head - Neck Cancer
What is Oral Cancer?
Head and neck cancer is a broad category that includes cancers originating in various regions of the head and neck, such as the mouth, throat, sinuses, and salivary glands. Other cancers, like those affecting the thyroid and pituitary glands, may also be considered part of this group.
These cancers can develop in the sinuses, nose, mouth (including the tongue, gums, and roof), throat (pharynx and larynx), lips, and, rarely, the salivary glands.
"Globally, head and neck cancers account for approximately 4.5% of all cancer diagnoses."
The seven types of head and neck cancers are as follows:
Symptoms of head and neck cancer
Symptoms of these cancers vary depending on their location. Mouth and throat symptoms may include a painless lump in the neck, a sore in the mouth that does not heal, coughing up blood, hoarseness or voice changes, loose teeth, and pain while swallowing. Nasal symptoms can include persistent nosebleeds and chronic nasal congestion or blockage. Other potential symptoms include a sore on the skin of the face, neck, or lips that does not heal, ear pain, and unintended weight loss. Recognizing these signs early and seeking medical evaluation is crucial for timely diagnosis and treatment.
Risk factors of head and neck cancer
Several factors increase the risk of head and neck cancer:
Preventive measures
The most effective way to prevent lung cancer is to avoid smoking entirely or quit if you currently smoke. Creating smoke-free environments at home and in your car is essential to protect both yourself and others from the harmful effects of tobacco.
High radon levels can also increase the risk of lung cancer, so testing your home for radon and implementing mitigation strategies can significantly reduce this risk.
Additionally, following health and safety guidelines to minimize exposure to harmful carcinogens—substances known to cause cancer—can further reduce the likelihood of developing lung cancer. Taking these preventive measures can help safeguard your lung health and lower your risk.quit smoking, if applicable.
